Lesson 2: Algebra
Algebra and Algebraic Expressions
Algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that extends arithmetic by using variables (symbols, often letters like ‘\(x\)’ and ‘\(y\)’. These letters represent change in quantities by describing relationship between these quantities using mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. For example, \(2x + 3y -z\)
Lets unpack those concepts.
Variable
A variable is represented by alphabets (generally in small letters) such as \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), \(d\), and so on, however, the most used variable is ‘\(x\)’. A expression without a variable is not an algebraic expression.
A variable, therefore, symbolizes a missing number that is intended to be known.
Coefficient
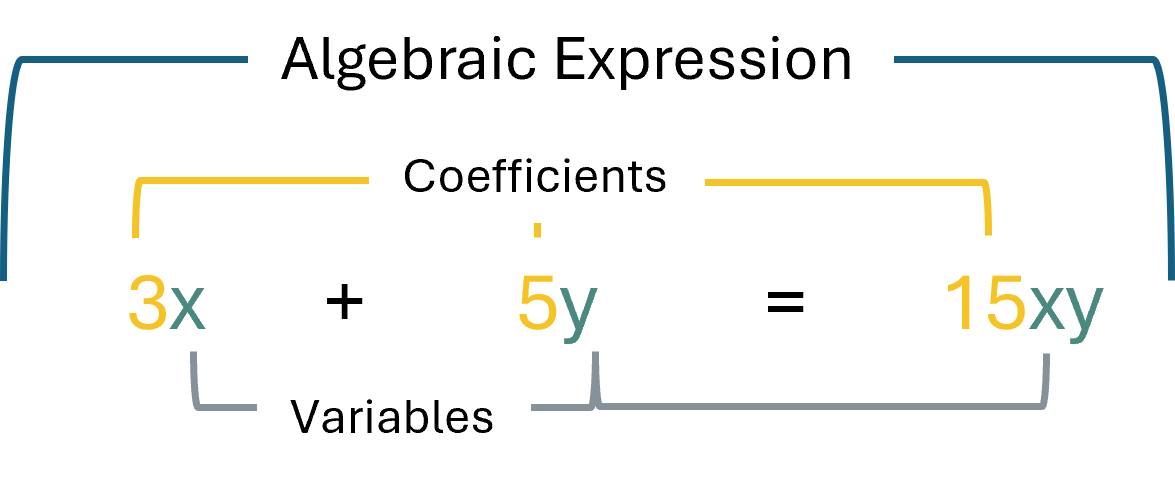
A coefficient is the numerical factor that multiplies with a variable in each term. For instance, in the above example, \(3\), \(5\), and \(15\) are coefficients of \(x\), \(y\) and \(xy\) variables respectively. in case where variable has no coefficient, treat that variable with the coefficient equal to '1'.
Exponent (or power)
A variable in any given term is also written in the form of something as a superscript of that variable such as \(x^2\) or \(x^3\). The superscript is called an ‘exponent’ or a ‘power’. The value of an exponent or power signifies the times a variable is multiplied by itself. For instance, \( x^2 = x \times x \) and \( x^3 = x \times x \times x \).
Remember: if power of any variable is '0', the value of that variable will always be equal to 1. i.e. \(x^0 = 1\)
Algebraic Expression
An algebraic expression is a combination of numbers (constants), letters (variables) and mathematical operators such as addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (x) or (division (÷). For example, \( 3x + 5 \), \(a^2 - 4\), \( \frac{2x}{5} \), and \(x=y-z\).
Algebraic expressions are written without equal (=) sign. Expression written with (=) sign are not mathematic equations. Therefore, \(x + y = 10\) or \(x + y = z\) are not algebraic expressions.
Constants
All numbers in an algebraic expression whether they are coefficient, exponents, or terms are constant as they have fixed value.
Terms
An algebraic expression has one, two or multiple terms. For instance, in \(3x + 5y = 15xy\) has three terms. i.e. \(3x\), \(5y\) and \(15xy\).
The terms in expression having similar variables and exponents are called 'like terms' or 'similar terms' For example, in expression \(2x^2 + 3y + x^2 - 5\) has two like terms i.e. \(2x^2\) and \(x^2\).
Terms only differs from the value of their coefficient. In above example, exponents of x are same but coefficients are not same.
Types of Algebraic Expressions based on the numbers of terms
Monomial
An algebraic expression that has only one term is call ‘Monomial Algebraic Expression’ It may include constants, variables or both. In such expressions mathematical operators are not used. For example, \(3x\), \(2a^2\), and \(7\).
Binomial
An algebraic expression that has two terms joined by a mathematic operator (+) or (-) is called ‘Binomial’ expression. The terms can be ‘like’ or ‘unlike’. For example, \(a + 3\), \(2a - 5b\), \(m^2+4m\).
Polynomial
As the word signifies, poly means ‘many’. So any expression that has more than one term is called ‘polynomial’ in general terms. For example, \(4^3+2^2-x+7\).
Find the value of ![]() where the value of
where the value of ![]()
Solution
From the question, we know
![]()
![]()
Insert the value of x in the algebraic expression
![]()
![]()
![]()
Remember: to solve such expressions, try combining the terms that are similar. Terms are said to be similar when they have same values for exponents or powers.
Simplify ![]()
As we can see terms with ![]() are similar, however, they have different coefficients.
are similar, however, they have different coefficients.
Therefore, we can combine them
![]()
![]()
Click 'Continue' to learn more on converting expressions into mathematical equations and understanding more about equations and their types.